Table of contents
Deep groove ball bearings
- Bearing design
- Load carrying capacity
- Compensation of angular misalignments
- Lubrication
- Sealing
- Speeds
- Noise
- Temperature range
- Cages
- Internal clearance
- Dimensions, tolerances
- Suffixes
- Structure of bearing designation
- Dimensioning
- Minimum load
- Design of bearing arrangements
- Mounting and dismounting
- Legal notice regarding data freshness
- Further information
Deep groove ball bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are available in single row and double row designs.
Single row bearings are particularly suitable where:
- high and very high speeds are required
- the bearing arrangement must be operated with very low friction
- very low running noise is required, without reducing the speed, load carrying capacity and operating life of the bearing (Generation C) ➤ link
- high demands are made on the sealing of the bearing, without increasing heat generation or limiting the speed (Generation C) ➤ section
- the bearing position is to be designed particularly economically
Double row bearings can be considered for bearing arrangements where:
- the load carrying capacity of single row deep groove ball bearings is no longer sufficient ➤ link
- axial loads in both directions and/or tilting moments must be supported in addition to radial loads ➤ link
- a high load carrying capacity is required and the design envelope available in a radial and axial direction is relatively small
|
Comparison of standard deep groove bearings with bearings of Generation C: running noise, frictional torque C = bearings of Generation C MR = frictional torque nG = limiting speed |
 |
Bearing design
Design variants
Single row deep groove ball bearings are available as:
- standard bearings ➤ Figure
- bearings of Generation C ➤ Figure and ➤ Figure
- matched bearing sets ➤ Figure
- corrosion-resistant bearings ➤ link
-
standard bearings ➤ Figure

Single row deep groove ball bearings are also available in many other designs and sizes, as well as for specific applications, by agreement. Corrosion-resistant bearings TPI 64, larger catalogue bearings GL 1.
Standard bearings
Proven and versatile bearings with high market shares
Single row deep groove ball bearings are self-retaining units, which are part of the group of radial ball bearings. The solid outer and inner rings have deep raceway grooves, with shoulders which are not generally interrupted by filling slots ➤ Figure. Solid cages made from polyamide PA66 or brass, and sheet metal cages made from steel or brass, are used as standard cages ➤ Table. The bearings are open or sealed. Due to the manufacturing processes used, open bearings, which are also available as sealed versions, can have turned recesses in the outer and inner ring for sealing washers or sealing shields.
Single row deep groove ball bearings are particularly versatile, robust in operation, easy to maintain and very economical. Due to their significant advantages, they are the most widely used rolling bearings worldwide. As a result, Schaeffler also manufactures these bearings in a large number of sizes and designs.
|
Single row deep groove ball bearings, Fr = radial load Fa = axial load
|
 |
Deep groove ball bearings of Generation C
Gen. C = optimised design of standard bearings
Deep groove ball bearings of Generation C correspond in their structure to single row standard deep groove ball bearings, but are specially optimised in relation to:
- significantly quieter running
- even more effective sealing
- a further reduction in the already very low frictional torque
Measures to reduce noise
Schaeffler has analysed the causes of noise generation in deep groove ball bearings using the most advanced methods. On the basis of the findings obtained from these analyses:
- The surface of the raceways has been improved
- The ball quality has been increased
- Osculation has been optimised
- The production tolerances have been reduced
- Deep groove ball bearings have been fitted with new riveted cages made from steel
The result of this is a noise reduction in Generation C bearings over comparable standard deep groove ball bearings.
The quality of the seal, together with the rating life, has a considerable influence on the efficiency of a rolling bearing. As a result, the seal must not only protect the running system reliably against contamination, the ingress of moisture and the loss of grease, but also ensure that the total frictional torque and heat generation in the bearing remains low despite the high sealing action. The new sealing shields, non-contact seals and contact seals of Generation C deep groove ball bearings (suffixes Z, BRS, HRS, ELS), demonstrate the success of Schaeffler in performing this difficult technical step effectively ➤ Figure and ➤ Figure. Description of sealing shields and seals ➤ section.
Gen. C = technical and economical advantages of very low friction
Electric motors, electrical machinery, washing machines, ventilators and electric tools are the preferred application areas of single row deep groove ball bearings. However, in order to facilitate further increases in the efficiency of these motors, machines and tools, the power loss occurring in the bearing arrangements must be reduced. The above-mentioned measures for reducing noise also resulted, for example, in an approximate reduction in friction of 35%, giving the designer a range of application-specific advantages:
- lower heat generation
- a longer grease operating life
- higher possible speeds
- a longer bearing operating life
- a reduced energy consumption
- lower energy costs
- lower overall cost of the bearing position
Gen. C = a leading player among single row deep groove ball bearings
In summary, this means that, in addition to their technical advantages, bearing positions with deep groove ball bearings of Generation C are also considerably more economical than bearing arrangements with single row standard deep groove ball bearings. Generation C is available in series 60, 62 and 63.
|
Single row deep groove ball bearings,
|
 |
|
Single row deep groove ball bearings,
|
 |
Matched bearing sets
Bearing sets in O, X or tandem arrangements
If the load carrying capacity of a single bearing is not sufficient, or the shaft is to be guided axially in both directions with a defined clearance, single row standard deep groove ball bearings are also available as matched bearing sets ➤ Figure.
As the arrangement of the bearing pairs is specific to the application, Schaeffler supplies bearing sets by agreement.
|
Matched bearing sets Fr = radial load Fa = axial load
|
 |
Corrosion-resistant bearings
Wide product range
Corrosion-resistant bearings are suitable where particular requirements for anti-corrosion protection are present. Schaeffler supplies deep groove ball bearings of this type in open and sealed designs.
The load carrying capacity for bearings made from corrosion-resistant steel is slightly lower than for bearings made from rolling bearing steel.
The range of these bearings and housings is described in detail in Technical Product Information TPI 64.
Double row deep groove ball bearings
Double row deep groove ball bearings of series 42 and 43 correspond in their structure and function to single row deep groove ball bearings arranged in pairs ➤ Figure. They have deep raceway grooves in the outer ring and a narrow osculation between the raceway grooves and balls. However, they are slightly narrower than two single row deep groove ball bearings of the series 62 and 63 with the same bore and outside diameter.
|
Double row deep groove ball bearing, Fr = radial load Fa = axial load |
 |
Load carrying capacity
Single row deep groove ball bearings – radial load carrying capacity
Suitable for predominantly radial loads
The balls are in contact with the raceways at one point only. Under purely radial load, the contact points between the rolling elements and raceways lie at the centre of the raceway. As a result, the connection between the contact points passes through the radial plane, i.e. the optimum load direction is a pure radial load ➤ Figure.
Larger bearing cross-sections permit higher loads
The load carrying capacity is dependent on the bearing series. As a result, deep groove ball bearings of series 618 and 619, with their smaller bearing cross-sections, cannot support loads as high as series 60, 62 and 63 – with identical dimensions relative to bore diameter d – with their larger cross-sections ➤ Figure.
|
Single row deep groove ball bearings, Cr = basic dynamic load rating |
 |
Single row deep groove ball bearings – axial load carrying capacity
Capable of supporting axial loads in both directions
Due to the deep raceway grooves in the bearing rings and the narrow osculation between the raceway grooves and balls, single row deep groove ball bearings can support axial loads in both directions ➤ Figure. The axial load carrying capacity is dependent, for example, on the bearing size, the internal construction and the operating clearance. If the axial load is too high, however, this can increase the running noise and considerably reduce the operating life of the bearings.
If there is any uncertainty regarding the axial load carrying capacity of the bearings, please consult Schaeffler.
Double row deep groove ball bearings
Considerably higher load carrying capacity than single row bearings
Due to the larger number of rolling elements, double row deep groove ball bearings can be subjected to greater loads than single row deep groove ball bearings. They can replace two single row deep groove ball bearings if a smaller design envelope width is required.
Also suitable for tilting moment loads
Double row deep groove ball bearings can also support tilting moment loads in addition to radial and axial loads ➤ Figure. They are therefore suitable for particularly short shafts that are supported by only one bearing.
|
Unilateral bearing arrangement of a shaft with a double row deep groove ball bearing (flying bearing arrangement) Fr = radial load Fa = axial load M = tilting moment load |
 |
Compensation of angular misalignments
Single row deep groove ball bearings – permissible adjustment angle
The adjustment angle is dependent on the magnitude of the load
Single row deep groove ball bearings are only suitable for compensating static angular misalignments to a very limited extent. As a result, the bearing positions must be well aligned. Misalignments shorten the operating life, as they place an additional strain on the bearing. In order to keep these loads at a low level, only small adjustment angles are permissible – dependent on the load – for deep groove ball bearings ➤ Table.
Permissible adjustment angles
|
Series |
Adjustment angle for |
|
|---|---|---|
|
low loads |
high loads |
|
|
62, 622, 63, 623, 64 |
5′ to 10′ |
8′ to 16′ |
|
618, 619, 160, 60 |
2′ to 6′ |
5′ to 10′ |
Double row deep groove ball bearings
Due to their internal construction, double row deep groove ball bearings do not have an angular adjustment facility. When using these bearings, therefore, misalignments are not permissible.
Lubrication
Single row deep groove ball bearings
Greased bearings are maintenance-free
Deep groove ball bearings sealed on both sides are lubricated with a high quality lithium soap grease with a mineral oil base, which has good anti‑corrosion characteristics. The grease filling is measured so that it is sufficient for the entire life of the bearing. As a result, these bearings are generally maintenance-free.
Do not wash greased bearings out prior to mounting. If mounting is carried out using thermal tools, the bearings should not be heated to a temperature in excess of +80 °C, taking account of the grease filling and seal material. If higher heating temperatures are required, it must be ensured that the permissible upper temperature limits for grease and seals are not exceeded. Schaeffler recommends the use of induction heating devices for heating purposes ➤ link.
Oil or grease lubrication is possible
Open bearings and bearings with seals on one side are not greased as standard. They must be lubricated with oil or grease. Lubrication is carried out via the end faces of the bearings.
Compatibility with plastic cages
When using bearings with plastic cages, compatibility between the lubricant and the cage material must be ensured if synthetic oils, lubricating greases with a synthetic oil base or lubricants containing a high proportion of EP additives are used.
Observe oil change intervals
Aged oil and additives in the oil can impair the operating life of plastics at high temperatures. As a result, stipulated oil change intervals must be strictly observed.
Double row deep groove ball bearings
Open bearings are greased
As standard, the bearings are lubricated with a high quality lithium soap grease with a mineral oil base and are maintenance-free for most applications.
Sealing
Single row deep groove ball bearings
The bearings are available in open and sealed designs
Single row deep groove ball bearings are available in open designs, as well as with seals on one or both sides ➤ Figure. In the case of sealed bearings, either non-contact or contact seals are used.
Provide additional seals in the adjacent construction
In the case of unsealed bearings, sealing of the bearing position must be carried out by the adjacent construction. The sealing system should reliably prevent:
- moisture and contaminants from entering the bearing
- the egress of lubricant from the bearing
Single row bearings with non-contact seals and sealing shields – standard bearings and Generation C
For bearing assemblies with high speeds and lower requirements for sealing
Non-contact seals are particularly suitable for applications with high speeds and high requirements for low heat generation ➤ Table. They are free from friction, except for a small amount of lubricant friction in the sealing gap. As a rule, non-contact seals do not undergo wear and therefore have an unlimited operating life. Deep groove ball bearings with non-contact seals on one or both sides have the suffixes RZ and 2RZ, or BRS and 2BRS; the suffixes Z and 2Z indicate seals on one or both sides with sealing shields.
Z sealing shields for standard bearings and for bearings of Gen. C
Z sealing shields are made from sheet steel. They sit securely in the outer ring and form a narrow, non-contact seal gap relative to the surface of the inner ring ➤ Table. This sealing arrangement is particularly suitable for applications with a rotating inner ring, high to very high speeds and low contamination impact.
RZ seals for standard bearings of series 618 and 619
RZ seals are rubberised sealing washers with a sheet steel reinforcement, which sit securely in the outer ring and form a narrow, non-contact seal gap relative to the surface of the inner ring ➤ Table.
BRS seals for bearings of Gen. C
BRS seals are rubberised sealing washers with a sheet steel reinforcement, which sit securely in the outer ring and form a narrow, non-contact seal gap relative to the surface of the inner ring ➤ Table. The seal is securely anchored in the outer ring. A recess incorporated in the inner ring forms a labyrinth in conjunction with the seal lip, which is filled with grease. The frictional behaviour of this seal is comparable with that of the Z sealing shield , however, the protection against ingress of dust and egress of lubricant is higher.
Single row bearings with non-contact seals – standard bearings and Generation C
For lower speeds and higher requirements for sealing action
As these seals are in contact with a defined contact pressure against their sliding surface, they provide very good sealing action against the egress of lubricant and ingress of moisture and dust. Attention must, however, be paid to the loss of energy resulting from friction at the sealing contact. Furthermore, in bearings with contact seals, the bearing speed is restricted by the permissible sliding velocity at the seal lip, i.e. the speed suitability of these bearings is lower than for open bearings or bearings with non-contact seals.
RSR seals, for standard bearings
RSR seals are elastomer lip seals with a sheet steel reinforcement ➤ Table. One seal lip is in radial contact with the inner ring.
HRS and ELS seals for bearings of Gen. C
HRS and ELS seals are securely anchored in a recess in the outer ring. The sealing material is vulcanised onto a sheet steel reinforcement ➤ Table. The sealing washer, together with the inner ring, forms an axial sealing system. In addition, the outer non-contact lip forms a protective labyrinth with the inner ring. An additional increase in the sealing action is also provided by the film of grease between the two seal lips. With this sealing arrangement, higher speeds can be achieved than with conventional RSR seals , as the frictional torque and thus the heat generation in the bearing is lower.
Generation C deep groove ball bearings with contact seals are supplied with HRS seals as standard. ELS seals are available for these bearings by agreement.
Seal characteristics – standard bearings and Generation C
|
Suffix |
Type of seal |
Seal characteristic |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
low-friction running |
high speeds |
sealing integrity against ingress of water |
sealing integrity against ingress of dust |
sealing integrity against loss of grease |
|||
|
‒ |
|
open, |
+++ |
+++ |
– |
– |
– |
|
Z, |
|
non-contact for standard bearings and Gen. C |
++ |
+++ |
o |
o |
o |
|
RZ, |
|
non-contact (elastomer), for standard bearings |
++ |
+++ |
o |
o |
o |
|
BRS, |
|
non-contact (elastomer), for Gen. C |
++ |
+++ |
o |
+ |
+ |
|
HRS, |
|
contact for Gen. C |
o |
+ |
++ |
++ |
++ |
|
RSR, |
|
contact for standard bearings |
o |
+ |
+ |
++ |
++ |
|
ELS, |
|
contact for Gen. C |
+ |
++ |
++ |
+++ |
+++ |
Double row deep groove ball bearings
The bearings are of an open design
Double row deep groove ball bearings are not sealed. As a result, sealing of the bearing position must be carried out by the adjacent construction ➤ section.
Speeds
Limiting speeds and reference speeds in the product tables
Two speeds are generally indicated in the product tables:
- the kinematic limiting speed nG
- the thermal speed rating nϑr
Limiting speeds
The limiting speed nG is the kinematically permissible speed of the bearing. Even under favourable mounting and operating conditions, this value should not be exceeded without prior consultation with Schaeffler ➤ link.
The values given in the product tables are valid for oil lubrication in the case of bearings without seals or shields and for grease lubrication where bearings are supplied greased and with seals or shields.
Values for grease lubrication
For grease lubrication, 85% of the value stated in the product tables is permissible in each case.
Reference speeds
nϑr is used to calculate nϑ
The thermal speed rating nϑr is not an application-oriented speed limit, but is a calculated ancillary value for determining the thermally safe operating speed nϑ ➤ link.
Bearings with contact seals
For bearings with contact seals, no speed ratings are defined in accordance with DIN ISO 15312:2004. As a result, only the limiting speed nG is given in the product tables for these bearings.
Speeds for bearing sets
For matched bearing pairs in an O, X or tandem arrangement, the speed must be limited to approx. 80% of the individual bearings. More accurate speed data for a specific application can be requested from Schaeffler.
Noise
The Schaeffler Noise Index (SGI) has been developed as a new feature for comparing the noise level of different bearing types and series. As a result, a noise evaluation of rolling bearings can now be carried out for the first time.
Schaeffler Noise Index
The SGI value is based on the maximum permissible noise level of a bearing in accordance with internal standards, which is calculated on the basis of ISO 15242. In order that different bearing types and series can be compared, the SGI value is plotted against the basic static load rating C0.
This permits direct comparisons between bearings with the same load carrying capacity. The upper limit value is given in each of the diagrams. This means that the average noise level of the bearings is lower than illustrated in the diagram.
The Schaeffler Noise Index is an additional performance characteristic in the selection of bearings for noise-sensitive applications. The specific suitability of a bearing for an application in terms of installation space, load carrying capacity or speed limit for example, must be checked independently of this.
|
Schaeffler Noise Index SGI = Schaeffler Noise Index C0 = basic static load rating |
 |
Temperature range
Limiting values
The operating temperature of the bearings is limited by:
- the dimensional stability of the bearing rings and rolling elements
- the cage
- the lubricant
- the seals
Possible operating temperatures of single row deep groove ball bearings ➤ Table.
Permissible temperature ranges
|
Operating temperature |
Open |
Sealed |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
with brass or |
with polyamide cage PA66 |
with seals |
with gap seals |
|
|
|
D ≦ 90 mm, |
–30 °C to +120 °C |
–30 °C to |
–30 °C to +120 °C, limited by |
|
90 mm < D ≦ 240 mm, –30 °C to +150 °C1) |
–30 °C to +120 °C | –30 °C to +110 °C, limited by the lubricant, cage material and seal material |
–30 °C to +120 °C, limited by the lubricant, cage material and seal material |
|
|
D > 240 mm, |
–30 °C to +120 °C | –30 °C to +110 °C, limited by the lubricant, cage material and seal material |
–30 °C to +120 °C, limited by the lubricant, cage material and seal material |
|
- By agreement, dimensionally stabilised for higher temperatures.
In the event of anticipated temperatures which lie outside the stated values, please contact Schaeffler.
Cages
Single row bearings: as standard, cages are made from sheet steel or are solid cages made from brass
Standard cages for single row deep groove ball bearings are made from sheet steel or brass ➤ Table. Other cage designs are available ➤ Table. With such cages, however, suitability for high speeds and temperatures as well as the basic load ratings may differ from the values for the bearings with standard cages.
Cage, cage suffix, bore code for single row deep groove ball bearings
|
Bearing series |
Sheet steel cage |
Sheet brass cage |
Solid brass cage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Y |
M |
||
|
Bore code |
|||
|
60 |
up to 34 |
‒ |
from 36 |
|
62 |
up to 30 |
‒ |
from 32 |
|
63 |
up to 26, 30 |
‒ |
28, from 32 |
|
64 |
up to 14 |
‒ |
from 15 |
|
160 |
up to 52 |
‒ |
from 56 |
|
618 |
up to 08, 26, |
09 to 24, |
from 60 |
|
619 |
up to 18, 21, |
‒ |
26 |
|
622 |
up to 12 |
‒ |
‒ |
|
623 |
up to 10 |
‒ |
‒ |
Double row bearings
Double row deep groove ball bearings have cages made from glass fibre reinforced polyamide PA66.
For high continuous temperatures and applications with difficult operating conditions, bearings with brass or sheet steel cages should be used. If there is any uncertainty regarding cage suitability, please consult Schaeffler.
Cages for bearings of Generation C
Riveted sheet metal cages used as standard
In bearings of Generation C, a noise-optimised, riveted sheet steel cage is used as the standard cage. This cage design does not have a cage suffix in the bearing designation.
The bearings are also available with cages made from glass fibre reinforced polyamide PA66 by agreement.
Internal clearance
Radial internal clearance
The standard is CN
Deep groove ball bearings of basic design and bearings of Generation C are manufactured as standard with radial internal clearance CN (normal) ➤ Table. CN is not stated in the designation.
The bearings are also available with the smaller internal clearance C2 and with the larger internal clearance C3 and C4.
CM also available for smaller bore diameters
Deep groove ball bearings with a bore diameter 10 ≦ d ≦ 50 are also available with the more closely toleranced bearing internal clearance CM (specifically for use in electric motors) ➤ Table.
The values for radial internal clearance (not CM) correspond to DIN 620‑4:2004 (ISO 5753-1:2009). They are valid for bearings which are free from load and measurement forces (without elastic deformation).
Radial internal clearance of deep groove ball bearings – standard bearings and Gen. C
|
Nominal |
Radial internal clearance |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
d |
C2 |
CN |
C3 |
C4 |
|||||
|
mm |
μm |
μm |
μm |
μm |
|||||
|
over |
incl. |
min. |
max. |
min. |
max. |
min. |
max. |
min. |
max. |
|
1.5 |
6 |
0 |
7 |
2 |
13 |
8 |
23 |
– |
– |
|
6 |
10 |
0 |
7 |
2 |
13 |
8 |
23 |
14 |
29 |
|
10 |
18 |
0 |
9 |
3 |
18 |
11 |
25 |
18 |
33 |
|
18 |
24 |
0 |
10 |
5 |
20 |
13 |
28 |
20 |
36 |
|
24 |
30 |
1 |
11 |
5 |
20 |
13 |
28 |
23 |
41 |
|
30 |
40 |
1 |
11 |
6 |
20 |
15 |
33 |
28 |
46 |
|
40 |
50 |
1 |
11 |
6 |
23 |
18 |
36 |
30 |
51 |
|
50 |
65 |
1 |
15 |
8 |
28 |
23 |
43 |
38 |
61 |
|
65 |
80 |
1 |
15 |
10 |
30 |
25 |
51 |
46 |
71 |
|
80 |
100 |
1 |
18 |
12 |
36 |
30 |
58 |
53 |
84 |
|
100 |
120 |
2 |
20 |
15 |
41 |
36 |
66 |
61 |
97 |
|
120 |
140 |
2 |
23 |
18 |
48 |
41 |
81 |
71 |
114 |
|
140 |
160 |
2 |
23 |
18 |
53 |
46 |
91 |
81 |
130 |
|
160 |
180 |
2 |
25 |
20 |
61 |
53 |
102 |
91 |
147 |
|
180 |
200 |
2 |
30 |
25 |
71 |
63 |
117 |
107 |
163 |
|
200 |
225 |
2 |
35 |
25 |
85 |
75 |
140 |
125 |
195 |
|
225 |
250 |
2 |
40 |
30 |
95 |
85 |
160 |
145 |
225 |
|
250 |
280 |
2 |
45 |
35 |
105 |
90 |
170 |
155 |
245 |
Radial internal clearance CM
|
Nominal |
Radial internal clearance |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
d |
CM |
||
|
mm |
μm |
||
|
over |
incl. |
min. |
max. |
|
10 |
18 |
4 |
11 |
|
18 |
24 |
5 |
12 |
|
24 |
30 |
5 |
12 |
|
30 |
40 |
9 |
17 |
|
40 |
50 |
9 |
17 |
Dimensions, tolerances
Dimension standards
The main dimensions of single row deep groove ball bearings correspond to DIN 625-1:2011. Nominal dimensions of single row deep groove ball bearings ➤ link.
The main dimensions of double row deep groove ball bearings correspond to DIN 625-3:2011. Nominal dimensions of double row deep groove ball bearings ➤ link.
Chamfer dimensions
The limiting dimensions for chamfer dimensions correspond to DIN 620‑6:2004. Overview and limiting values ➤ section. Nominal value of chamfer dimension ➤ link.
Tolerances for standard bearings
The tolerances for the dimensional and running accuracy of single and double row standard bearings correspond to tolerance class Normal in accordance with ISO 492:2014. Bearings with a higher accuracy are available by agreement. Tolerance values in accordance with ISO 492 ➤ link.
The width tolerance of matched bearings deviates from the values in the above-mentioned standard ➤ Table.
Width tolerance of bearing rings in matched bearings
|
Nominal d |
Width deviation tΔBs |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
mm |
μm |
||
|
over |
incl. |
U |
L |
|
‒ |
18 |
0 |
–250 |
|
18 |
50 |
0 |
–300 |
|
50 |
80 |
0 |
–450 |
|
80 |
120 |
0 |
–550 |
|
120 |
180 |
0 |
–750 |
|
180 |
250 |
0 |
–950 |
|
250 |
315 |
0 |
–1 050 |
Tolerance symbols ➤ Table
U = upper limit deviation
L = lower limit deviation
Tolerances for bearings of Generation C
The dimensional and running tolerances correspond to tolerance class 6 in accordance with ISO 492:2014. Bearings with a higher accuracy are available by agreement. Tolerance values in accordance with ISO 492 ➤ Table.
Suffixes
For a description of the suffixes used in this chapter see ➤ Table, ➤ Table and medias interchange http://www.schaeffler.de/std/1B69.
Further special designs of deep groove ball bearings are available by agreement.
Suffixes and corresponding descriptions, single row deep groove ball bearings
|
Suffix |
Description of suffix |
|
|---|---|---|
|
C |
Deep groove ball bearing, Generation C |
Standard |
|
M |
Solid brass cage, ball-guided |
Standard |
|
MA |
Solid brass cage, guided on outer ring rib |
Available by agreement |
|
MB |
Solid brass cage, guided on inner ring rib |
Available by agreement |
|
C2 |
Radial internal clearance C2 (smaller than normal) |
Available by agreement |
|
C3 |
Radial internal clearance C3 (larger than normal) |
Available by agreement |
|
C4 |
Radial internal clearance C4 (larger than C3) |
Available by agreement |
|
CM |
Radial internal clearance more closely toleranced than normal |
Available by agreement |
|
2BRS |
Non-contact seal on both sides (labyrinth seal) |
Standard for Generation C |
|
2HRS |
Contact seal on both sides (lip seal) |
Standard for Generation C |
|
2RSR |
Contact seal on both sides (lip seal) |
Standard |
|
2RZ |
Non-contact seal on both sides (rubberised gap seal) |
Standard |
|
2Z |
Non-contact sealing shield on both sides (sheet metal gap seal) |
Standard |
|
BRS |
Non-contact seal on one side (labyrinth seal) |
Available by agreement |
|
ELS |
Contact seal on one side (lip seal) |
Available by agreement for Generation C |
|
2ELS |
Contact seal on both sides (lip seal) |
Available by agreement for Generation C |
|
RSR |
Contact seal on one side (lip seal) |
Available by agreement |
|
RZ |
Non-contact seal on one side (rubberised gap seal) |
Available by agreement |
|
TVH |
Solid cage made from glass fibre reinforced polyamide PA66 |
Available by agreement |
|
Y |
Sheet brass cage |
Available by agreement |
|
Z |
Non-contact sealing shield on one side (sheet metal gap seal) |
Available by agreement |
|
S0 |
Dimensionally stabilised bearing for operating temperatures up to +150 °C |
Available by agreement |
|
S1 |
Dimensionally stabilised bearing for operating temperatures up to +200 °C |
Available by agreement |
|
S2 |
Dimensionally stabilised bearing for operating temperatures up to +250 °C |
Available by agreement |
Suffixes and corresponding descriptions, double row deep groove ball bearings
|
Suffix |
Description of suffix |
|
|---|---|---|
|
B |
Modified internal construction |
Standard |
|
TVH |
Solid cage made from glass fibre reinforced polyamide PA66 |
Standard |
Structure of bearing designation
Examples of composition of bearing designation
The designation of bearings follows a set model. Examples ➤ Figure, ➤ Figure and ➤ Figure. The composition of designations is subject to DIN 623-1 ➤ Link.
|
Single row deep groove ball bearing, |
 |
|
Single row deep groove ball bearing, |
 |
|
Double row deep groove ball bearing, |
 |
Dimensioning
Equivalent dynamic bearing load
P = Fr under purely radial load of constant magnitude and direction
The basic rating life equation L = (Cr/P)p used in the dimensioning of bearings under dynamic load assumes a load of constant magnitude and direction. In radial bearings, this is a purely radial load Fr. If this condition is met, the bearing load Fr is used in the rating life equation for P (P = Fr).
P is a substitute force for combined load and various load cases
If this condition is not met, a constant radial force must first be determined for the rating life calculation that (in relation to the rating life) represents an equivalent load. This force is known as the equivalent dynamic bearing load P.
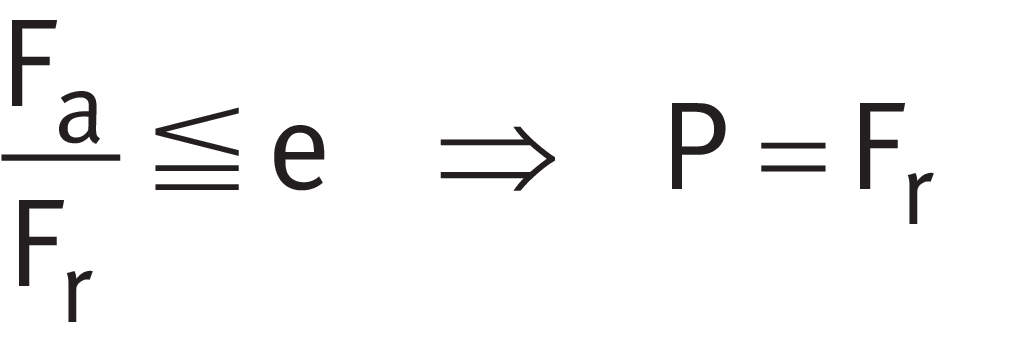
Fa/Fr ≦ e or Fa/Fr > e
The calculation of P is dependent on the load ratio Fa/Fr and the calculation factor e ➤ Equation and ➤ Equation.
Equivalent dynamic load
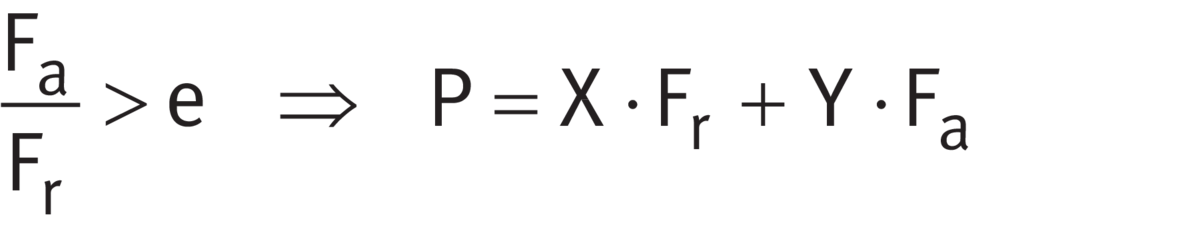
Legend
| P | N |
Equivalent dynamic bearing load |
| Fr | N |
Radial load |
| Fa | N |
Axial load |
| e, X, Y | – |
factors ➤ Table |
The values in accordance with ➤ Table are valid for normal fits (shaft manufactured to j5 or k5, housing bore manufactured to J6). If the calculation values lie between the stated values (e.g. in the case of 0,4), then read off the table values for 0,3 and 0,5 and determine the intermediate values using linear interpolation.
Factors e, X and Y
|
|
Factor for radial internal clearance |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
CN |
|||
|
e |
X |
Y |
|
|
0,3 |
0,22 |
0,56 |
2 |
|
0,5 |
0,24 |
0,56 |
1,8 |
|
0,9 |
0,28 |
0,56 |
1,58 |
|
1,6 |
0,32 |
0,56 |
1,4 |
|
3 |
0,36 |
0,56 |
1,2 |
|
6 |
0,43 |
0,56 |
1 |
Legend
| C0r | N |
Basic static load rating ➤ link |
| f0 | - |
Factor |
| Fa | N |
Axial load |
Equivalent static bearing load
F0a/F0r ≦ 0,8 or F0a/F0r > 0,8
For deep groove ball bearings under static loading ➤ Equation and ➤ Equation. The calculation of P0 is dependent on the load ratio F0a/F0r and the factor 0,8.
Equivalent static load

Equivalent static load
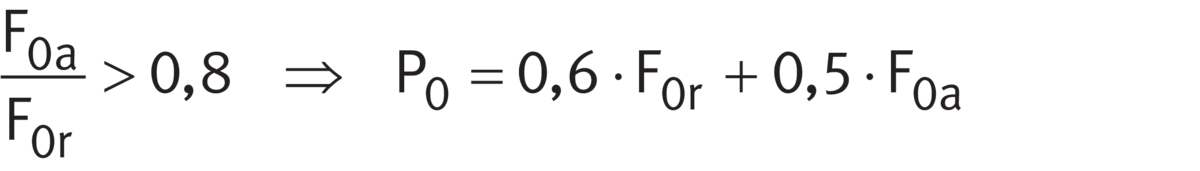
Legend
| P0 | N |
Equivalent static bearing load |
| F0r, F0a | N |
Largest radial or axial load present (maximum load) |
Static load safety factor
S0 = C0/P0
In addition to the basic rating life L (L10h), it is also always necessary to check the static load safety factor S0 ➤ Equation.
Static load safety factor
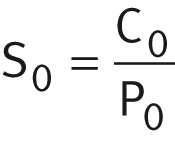
Legend
| S0 | - |
Static load safety factor |
| C0 | N |
Basic static load rating |
| P0 | N |
Equivalent static bearing load |
Minimum load
In order to prevent damage due to slippage, a minimum radial load of P > C0r/100 is required
In order that slippage does not occur between the contact partners, the deep groove ball bearings must be constantly subjected to a sufficiently high load. Based on experience, a minimum radial load of the order of P > C0r/100 is necessary for this purpose. In most cases, however, the radial load is higher than the requisite minimum load due to the weight of the supported parts and the external forces.
If the minimum radial load is lower than indicated above, please consult Schaeffler.
Design of bearing arrangements
Support bearing rings over their entire circumference and width
In order to allow full utilisation of the load carrying capacity of the bearings and thus also achieve the requisite rating life, the bearing rings must be rigidly and uniformly supported by means of contact surfaces over their entire circumference and over the entire width of the raceway. The seating and contact surfaces should not be interrupted by grooves, holes or other recesses. The accuracy of mating parts must meet specific requirements ➤ Table to ➤ Table.
Radial location of bearings – fit recommendations
For secure radial location, tight fits are necessary
In addition to supporting the rings adequately, the bearings must also be securely located in a radial direction, to prevent creep of the bearing rings on the mating parts under load. This is generally achieved by means of tight fits between the bearing rings and the mating parts. If the rings are not secured adequately or correctly, this can cause severe damage to the bearings and adjacent machine parts. Influencing factors, such as the conditions of rotation, magnitude of the load, internal clearance, temperature conditions, design of the mating parts and the mounting and dismounting options must be taken into consideration in the selection of fits.
If shock type loads occur, tight fits (transition fit or interference fit) are required to prevent the rings from coming loose at any point. Clearance, transition or interference fits ➤ link.
The following information provided in Technical principles must be taken into consideration in the design of bearing arrangements:
- conditions of rotation ➤ link
- tolerance classes for cylindrical shaft seats (radial bearings) ➤ link
- shaft fits ➤ link
- tolerance classes for bearing seats in housings (radial bearings) ➤ link
- housing fits ➤ link
Axial location of bearings – location methods
The bearings must also be securely located in an axial direction
As a tight fit alone is not normally sufficient to also locate the bearing rings securely on the shaft and in the housing bore in an axial direction, this must usually be achieved by means of an additional axial location or retention method. The axial location of the bearing rings must be matched to the type of bearing arrangement. Shaft and housing shoulders, housing covers, nuts, spacer rings and retaining rings etc., are fundamentally suitable.
Axial adjustment by means of spring element to reduce noise
Example: single row deep groove ball bearing, bearing arrangement in an electric motor
If the bearing arrangement is to run particularly quietly, this can be achieved economically with commonly available spring elements ➤ Figure. The bearings in the figure must only support guidance forces in an axial direction. The inner rings have a tight fit on the shaft and are abutted on the shaft shoulders. The outer rings are mounted with a sliding seat. A spring washer is fitted between the outer ring of the right hand bearing and the cover collar. The bearings are thus axially adjusted by the tensioned springs. This achieves particularly smooth running.
|
Bearing arrangement axially adjusted with a spring washer
|
 |
Dimensional, geometrical and running accuracy of the bearing seats
For bearings with tolerance class Normal, a minimum of IT6 should be provided for the shaft seat and a minimum of IT7 for the housing seat
The accuracy of the cylindrical bearing seat on the shaft and in the housing should correspond to the accuracy of the bearing used. For deep groove ball bearings with the tolerance class Normal, the shaft seat should correspond to a minimum of standard tolerance grade IT6 and the housing seat to a minimum of IT7; with tolerance class 6, the shaft seat should correspond to a minimum of IT5 and the housing seat to a minimum of IT6. Guide values for the geometrical and positional tolerances of bearing seating surfaces ➤ Table, tolerances t1 to t3 in accordance with ➤ link. Numerical values for IT grades ➤ Table.
Guide values for the geometrical and positional tolerances of bearing seating surfaces
|
Bearing |
Bearing seating surface |
Standard tolerance grades to ISO 286-1 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
to ISO 492 |
to DIN 620 |
Diameter tolerance |
Roundness tolerance |
Parallelism tolerance |
Total axial runout tolerance of abutment shoulders |
|
|
t1 |
t2 |
t3 |
||||
|
Normal |
PN (P0) |
Shaft |
IT6 (IT5) |
Circumferential load IT4/2 |
Circumferential load IT4/2 |
IT4 |
| Shaft | IT6 (IT5) |
Point load IT5/2 |
Point load IT5/2 |
IT4 | ||
|
Housing |
IT7 (IT6) |
Circumferential load IT5/2 |
Circumferential load IT5/2 |
IT5 |
||
| Housing | IT7 (IT6) |
Point load IT6/2 |
Point load IT6/2 |
IT5 | ||
|
6 |
P6 |
Shaft |
IT5 |
Circumferential load IT3/2 |
Circumferential load IT3/2 |
IT3 |
| Shaft | IT5 |
Point load IT4/2 |
Point load IT4/2 |
IT3 | ||
|
Housing |
IT6 |
Circumferential load IT4/2 |
Circumferential load IT4/2 |
IT4 |
||
| Housing | IT6 |
Point load IT5/2 |
Point load IT5/2 |
IT4 | ||
Numerical values for ISO standard tolerances (IT grades) to ISO 286-1:2010
|
IT grade |
Nominal dimension in mm |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
over |
– |
3 |
6 |
10 |
18 |
30 |
50 |
80 |
|
|
incl. |
3 |
6 |
10 |
18 |
30 |
50 |
80 |
120 |
|
|
Values in μm |
|||||||||
|
IT3 |
2 |
2,5 |
2,5 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
IT4 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
10 |
|
|
IT5 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
8 |
9 |
11 |
13 |
15 |
|
|
IT6 |
6 |
8 |
9 |
11 |
13 |
16 |
19 |
22 |
|
|
IT7 |
10 |
12 |
15 |
18 |
21 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
|
|
continued ▼ |
|||||||||
Numerical values for ISO standard tolerances (IT grades) to ISO 286-1:2010
|
IT grade |
Nominal dimension in mm |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
over |
120 |
180 |
250 |
315 |
400 |
500 |
630 |
800 |
|
|
incl. |
180 |
250 |
315 |
400 |
500 |
630 |
800 |
1 000 |
|
|
Values in μm |
|||||||||
|
IT3 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
13 |
15 |
16 |
18 |
21 |
|
|
IT4 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
18 |
20 |
22 |
25 |
28 |
|
|
IT5 |
18 |
20 |
23 |
25 |
27 |
32 |
36 |
40 |
|
|
IT6 |
25 |
29 |
32 |
36 |
40 |
44 |
50 |
56 |
|
|
IT7 |
40 |
46 |
52 |
57 |
63 |
70 |
80 |
90 |
|
|
continued ▲ |
|||||||||
Roughness of cylindrical bearing seating surfaces
Ra must not be too high
The roughness of the bearing seats must be matched to the tolerance class of the bearings. The mean roughness value Ra must not be too high, in order to maintain the interference loss within limits. The shafts must be ground, while the bores must be precision turned. Guide values as a function of the IT grade of bearing seating surfaces ➤ Table.
Roughness values for cylindrical bearing seating surfaces – guide values
|
Nominal diameter d (D) |
Recommended mean roughness value Ramax |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mm |
μm |
||||
|
Diameter tolerance (IT grade) |
|||||
|
over |
incl. |
IT7 |
IT6 |
IT5 |
IT4 |
|
‒ |
80 |
1,6 |
0,8 |
0,4 |
0,2 |
|
80 |
500 |
1,6 |
1,6 |
0,8 |
0,4 |
|
500 |
1 250 |
3,21) |
1,6 |
1,6 |
0,8 |
- For the mounting of bearings using the hydraulic method, a value Ra = 1,6 μm must not be exceeded.
Mounting dimensions for the contact surfaces of bearing rings
The contact surfaces for the rings must be of sufficient height
The mounting dimensions of the shaft and housing shoulders, and spacer rings etc., must ensure that the contact surfaces for the bearing rings are of sufficient height. However, they must also reliably prevent rotating parts of the bearing from grazing stationary parts. Proven mounting dimensions for the radii and diameters of the abutment shoulders are indicated in the product tables. These dimensions are limiting dimensions (maximum or minimum dimensions); the actual values should not be higher or lower than specified.
Mounting and dismounting
The mounting and dismounting options for deep groove ball bearings, by thermal, hydraulic or mechanical methods, must also be taken into consideration in the design of the bearing position.
Ensure that the bearings are not damaged during fitting.
Deep groove ball bearings are not separable. In the mounting of non‑separable bearings, the mounting forces must always be applied to the bearing ring with a tight fit.
Schaeffler Mounting Handbook
Rolling bearings must be handled with great care
Rolling bearings are well-proven precision machine elements for the design of economical and reliable bearing arrangements, which offer high operational security. In order that these products can function correctly and achieve the envisaged operating life without detrimental effect, they must be handled with care.
The Schaeffler Mounting Handbook MH 1 gives comprehensive information about the correct storage, mounting, dismounting and maintenance of rotary rolling bearings http://www.schaeffler.de/std/1B68. It also provides information which should be observed by the designer, in relation to the mounting, dismounting and maintenance of bearings, in the original design of the bearing position. This book is available from Schaeffler on request.
Legal notice regarding data freshness
The further development of products may also result in technical changes to catalogue products
Of central interest to Schaeffler is the further development and optimisation of its products and the satisfaction of its customers. In order that you, as the customer, can keep yourself optimally informed about the progress that is being made here and with regard to the current technical status of the products, we publish any product changes which differ from the printed version in our electronic product catalogue.
We therefore reserve the right to make changes to the data and illustrations in this catalogue. This catalogue reflects the status at the time of printing. More recent publications released by us (as printed or digital media) will automatically precede this catalogue if they involve the same subject. Therefore, please always use our electronic product catalogue to check whether more up-to-date information or modification notices exist for your desired product.
Further information
In addition to the data in this chapter, the following chapters in Technical principles must also be observed in the design of bearing arrangements: